Introduction:
All businesses are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency. One approach that has gained significant traction in recent years is Offshore Development Services. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of offshore development, exploring what it entails, its benefits, challenges, and best practices.
Understanding Offshore Development Services
Offshore development refers to the practice of Outsourcing Software Development tasks to a team located in a different country. This model has become increasingly popular due to its potential cost savings, access to a global talent pool, and round-the-clock development capabilities.
Benefits of Offshore Software Development Services

1. Cost Efficiency:
One of the primary reasons businesses opt for Offshore Software Development is cost savings. By leveraging talent from countries with lower labor costs, companies can significantly reduce their development expenses without compromising on quality.
One of the primary reasons businesses opt for Offshore Software Development is cost savings. By leveraging talent from countries with lower labor costs, companies can significantly reduce their development expenses without compromising on quality.
2. Access to Global Talent Pool:
Our Offshore Development Service allows businesses to tap into a diverse talent pool spanning the globe. This means access to specialized skills and expertise that may not be readily available locally.
Our Offshore Development Service allows businesses to tap into a diverse talent pool spanning the globe. This means access to specialized skills and expertise that may not be readily available locally.
3. Faster Time-to-Market:
With teams working across different time zones, offshore development enables round-the-clock productivity. This can lead to faster development cycles and quicker time-to-market for products and services.
With teams working across different time zones, offshore development enables round-the-clock productivity. This can lead to faster development cycles and quicker time-to-market for products and services.
4. Scalability:
Offshore Development Services offer scalability, allowing businesses to quickly ramp up or downsize their development teams based on project requirements. This flexibility is particularly valuable in dynamic market environments.
Offshore Development Services offer scalability, allowing businesses to quickly ramp up or downsize their development teams based on project requirements. This flexibility is particularly valuable in dynamic market environments.
5. Focus on Core Competencies:
By outsourcing non-core development tasks, businesses can focus their internal resources and expertise on strategic initiatives and core competencies, thereby enhancing overall competitiveness.
By outsourcing non-core development tasks, businesses can focus their internal resources and expertise on strategic initiatives and core competencies, thereby enhancing overall competitiveness.
6. Risk Mitigation:
Offshore development providers often have robust risk management processes in place, helping businesses mitigate potential risks associated with development projects.
Offshore development providers often have robust risk management processes in place, helping businesses mitigate potential risks associated with development projects.
Challenges of Offshore Development Services

While Offshore Development Offers Numerous Benefits, It Also Comes with Its Fair Share of Challenges. These May Include:
1. Communication Barriers:
Differences in time zones, cultural nuances, and language barriers can sometimes hinder effective communication between offshore teams and clients.
Differences in time zones, cultural nuances, and language barriers can sometimes hinder effective communication between offshore teams and clients.
2. Quality Control:
Ensuring consistent quality across distributed teams can be challenging. Effective quality control mechanisms and regular communication are essential to address this challenge.
Ensuring consistent quality across distributed teams can be challenging. Effective quality control mechanisms and regular communication are essential to address this challenge.
3. Intellectual Property Protection:
Offshore development involves sharing sensitive intellectual property with external parties, raising concerns about data security and intellectual property protection. It’s crucial to establish clear legal frameworks and security protocols to address these concerns.
Offshore development involves sharing sensitive intellectual property with external parties, raising concerns about data security and intellectual property protection. It’s crucial to establish clear legal frameworks and security protocols to address these concerns.
4. Project Management Complexity:
Managing projects across geographically dispersed teams requires robust project management processes and tools to ensure coordination, collaboration, and accountability.
Managing projects across geographically dispersed teams requires robust project management processes and tools to ensure coordination, collaboration, and accountability.
What Does an Offshore Developer DO?
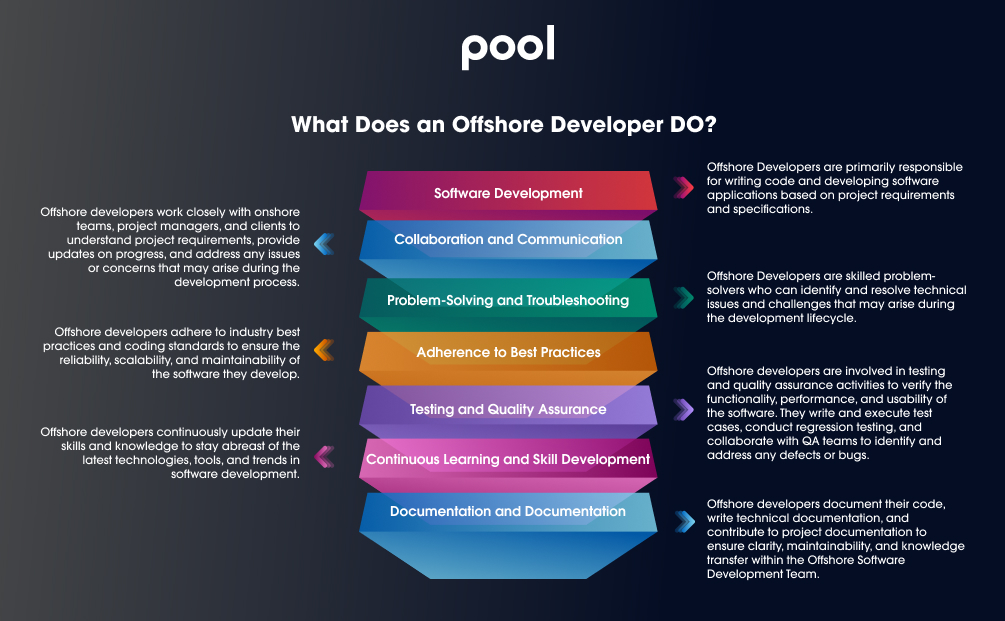
1. Software Development:
Offshore Developers are primarily responsible for writing code and developing software applications based on project requirements and specifications. They utilize programming languages, frameworks, and development tools to create functional and efficient software solutions.
Offshore Developers are primarily responsible for writing code and developing software applications based on project requirements and specifications. They utilize programming languages, frameworks, and development tools to create functional and efficient software solutions.
2. Collaboration and Communication:
Offshore developers work closely with onshore teams, project managers, and clients to understand project requirements, provide updates on progress, and address any issues or concerns that may arise during the development process. Effective communication and collaboration are essential for successful offshore development projects.
Offshore developers work closely with onshore teams, project managers, and clients to understand project requirements, provide updates on progress, and address any issues or concerns that may arise during the development process. Effective communication and collaboration are essential for successful offshore development projects.
3. Problem-Solving and Troubleshooting:
Offshore Developers are skilled problem-solvers who can identify and resolve technical issues and challenges that may arise during the development lifecycle. They leverage their expertise and knowledge to troubleshoot issues, optimize code, and ensure the overall quality and performance of the software.
Offshore Developers are skilled problem-solvers who can identify and resolve technical issues and challenges that may arise during the development lifecycle. They leverage their expertise and knowledge to troubleshoot issues, optimize code, and ensure the overall quality and performance of the software.
4. Adherence to Best Practices:
Offshore developers adhere to industry best practices and coding standards to ensure the reliability, scalability, and maintainability of the software they develop. They follow established coding conventions, utilize version control systems, and participate in code reviews to uphold quality standards.
Offshore developers adhere to industry best practices and coding standards to ensure the reliability, scalability, and maintainability of the software they develop. They follow established coding conventions, utilize version control systems, and participate in code reviews to uphold quality standards.
5. Testing and Quality Assurance:
Offshore developers are involved in testing and quality assurance activities to verify the functionality, performance, and usability of the software. They write and execute test cases, conduct regression testing, and collaborate with QA teams to identify and address any defects or bugs.
Offshore developers are involved in testing and quality assurance activities to verify the functionality, performance, and usability of the software. They write and execute test cases, conduct regression testing, and collaborate with QA teams to identify and address any defects or bugs.
6. Continuous Learning and Skill Development:
Offshore developers continuously update their skills and knowledge to stay abreast of the latest technologies, tools, and trends in software development. They participate in training programs, workshops, and professional development activities to enhance their proficiency and expertise.
Offshore developers continuously update their skills and knowledge to stay abreast of the latest technologies, tools, and trends in software development. They participate in training programs, workshops, and professional development activities to enhance their proficiency and expertise.
7. Documentation and Documentation: Offshore developers document their code, write technical documentation, and contribute to project documentation to ensure clarity, maintainability, and knowledge transfer within the Offshore Software Development Team. Documentation helps streamline the development process and facilitate collaboration among team members.
Offshore Software Development Best Practices
To Maximize the Benefits of Offshore Development Services and Mitigate Potential Challenges, Consider the Following Best Practices:
1. Clear Communication Channels:
Establish clear and open communication channels between offshore teams and clients. Leverage video conferencing, collaboration tools, and regular progress updates to foster transparency and alignment.
Establish clear and open communication channels between offshore teams and clients. Leverage video conferencing, collaboration tools, and regular progress updates to foster transparency and alignment.
2. Define Clear Objectives and Expectations:
Clearly define project objectives, requirements, and expectations upfront to avoid misunderstandings and scope creep later in the development process.
Clearly define project objectives, requirements, and expectations upfront to avoid misunderstandings and scope creep later in the development process.
3. Cultural Sensitivity and Awareness:
Foster cultural sensitivity and awareness within your teams to bridge cultural gaps and build strong working relationships across borders.
Foster cultural sensitivity and awareness within your teams to bridge cultural gaps and build strong working relationships across borders.
4. Invest in Quality Assurance:
Implement robust quality assurance processes to ensure consistent quality across all stages of development. This may include code reviews, testing automation, and continuous integration practices.
Implement robust quality assurance processes to ensure consistent quality across all stages of development. This may include code reviews, testing automation, and continuous integration practices.
5. Protect Intellectual Property:
Establish comprehensive legal agreements and security protocols to protect sensitive intellectual property and data throughout the development lifecycle.
Establish comprehensive legal agreements and security protocols to protect sensitive intellectual property and data throughout the development lifecycle.
6. Build Strong Partnerships:
Choose Offshore Development Partner who align with your values, goals, and working culture. Building strong partnerships based on trust and collaboration is key to successful offshore engagements.
Choose Offshore Development Partner who align with your values, goals, and working culture. Building strong partnerships based on trust and collaboration is key to successful offshore engagements.
Conclusion
Offshore Development Services offer compelling benefits for businesses looking to accelerate their software development initiatives, reduce costs, and access global talent. By understanding the potential benefits, challenges, and best practices associated with Offshore Development, businesses can make informed decisions and effectively leverage offshore resources to drive innovation and growth in today’s competitive marketplace.
